Preface
China and Madagascar have strong complementarity in economic and trade cooperation, which means huge development space. Sino-Madagascar economic and trade cooperation starts from scratch, the fields of which have generally expanded and the base of which has become increasingly solid. In the three episodes, we will introduce to you information about investment, the foreign trade of Madagascar, and the economic cooperation between China and Madagascar. Now, let's watch Episode 2 - Foreign Trade of the Republic of Madagascar.
Foreign Trade in Madagascar
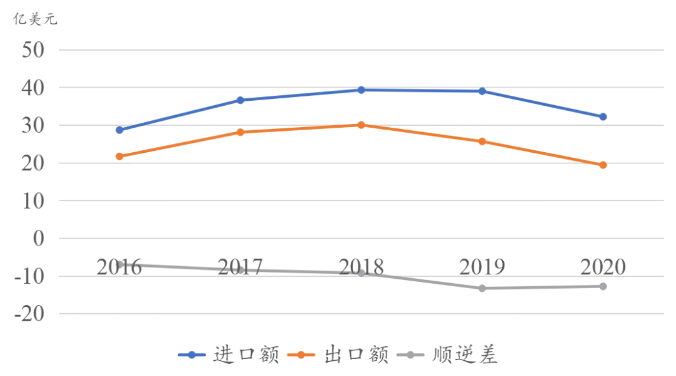
From 2016 to 2020, Madagascar's export volume was between USD 1.9-3.1 billion, whereas its import volume was between USD 2.7-4 billion, with a long-term trade deficit.
Madagascar's export products are mainly agricultural (e.g. vanilla) and resource-based products (e.g. ore).
Madagascar's import products are mainly resource-based (e.g. medium oil, light oil) and non-resource products (e.g. rice, wheat and flour).
Madagascar's Foreign Trade Regulations and Policies
▼
● Department in Charge of Trade
The Ministry of Industry, Commerce and Handicrafts is the government department in charge of commerce, investment and trade in Madagascar, and its main responsibility includes formulating development policies for trade, industry and handicraft industry for both within and outside the country, as well as implementation, coordination, tracking and evaluation for the policies. Under the Ministry of Industry, Commerce and Handicrafts, there are the General Department of Industrialization, the General Department of Commerce and the General Department of Handicrafts. The General Department of Commerce is composed of the Department of Domestic Trade, the Department of Consumer Protection, the Department of Foreign Trade, etc. And the Department of Foreign Trade has the Division of Service Trade Development, the Division of Import, the Division of Export Promotion, and the Division of International Relations and Economic Integration.
The Ministry of Foreign Affairs is responsible for bilateral and multilateral affairs related to trade.
The Ministry of Economy and Finance is in charge of affairs such as customs and taxation
● Trade Regulations System
Madagascar's main trade laws are the Company Law (Loi N° 2003-036 du 30 janvier 2004 sur les Sociétés Commerciales), the Investment Law (Loi N° 2007-036 du 14 janvier 2008 sur les Investissements à Madagascar), the Customs Law (Code des Douanes), etc.. Visit the website of the Economic and Commercial Office of the Chinese Embassy in Madagascar for relevant laws and regulations in the section of "Politiques & Lois".
Administrative Regulations of Trade
All economic entities in Madagascar enjoy equal rights in foreign economic and trade activities. The company can freely manage the enterprise in accordance with its own Articles of Association. Enterprises are free to engage in investment and trade activities subject to compliance with the laws and regulations of Madagascar. Except for a few rare varieties that are restricted, the rest of the commodities are entitled to liberalized operation.
Import management: To promote imports, Madagascar implements duty-free treatment for certain commodities, including medicines, fertilizers (mineral fertilizers, chemical fertilizers and animal fertilizers), walking tractors, etc. There is no limit for import quotas in Madagascar so far.
Export restrictions: In March 2010, the government of Madagascar issued a decree banning the logging and export of redwood and ebony in Madagascar. Anyone who logs and exports redwood and ebony in Madagascar will be held criminally liable. In addition, many rare plants and animals in Madagascar are also subject to restricted export resources.
● Tariff System
According to the customs tariff issued by Madagascar Customs, there are three main categories of import duties, most of which are AD Valorem duties:
(1) The tariff on imported raw materials is 5%-10%.
(2) The tariff on imported machines and spare parts is 10% (e.g. electric locomotives, passenger coaches, train coaches and postal coaches, household appliances, etc.).
(3) The tariff on imported manufactured and processed products is 20% (e.g., clothing, etc.).
The main commodities exempted from import duties are rice and paddy rice; vegetable seeds; fertilizers (mineral, chemical and animal fertilizers) and various pesticides; agricultural machinery; wind turbine equipment, etc.
Sino-Madagascar Bilateral Trade
In 2020, Madagascar's total export to China was USD 120 million, and the total import from China was USD 820 million. There is a long-term trade deficit with China.

Madagascar mainly exports ore and other resource-based products to China, while the export volume of high value-added non-resource products is low, so there is a broad market space.
Madagascar mainly imports products such as wool, rice, and clothing from China.
Sino-Madagascar Economic and Trade Outlook
The governments of China and Madagascar signed a trade agreement in 1974; an agreement on trade, economic and technical cooperation in June 1995; and an agreement on the establishment of a mixed economic and trade commission and bilateral investment protection in 2005. In November 2019, a delegation of the Department of West Asia and Africa of the Ministry of Commerce visited Madagascar and exchanged views with Madagascar on topics such as implementing the "Eight Actions" of the Beijing Summit of the Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC) and promoting bilateral economic and trade cooperation.
At present, Hunan Province is committed to building the Africa Non-resource Products Distribution and Trading Center. With this background, China can increase the import of high-value-added non-resource products originated in Madagascar, such as fruit and vanilla, and give preferential policies in terms of market access and tariff, by referring to the practices of developed countries such as Europe and the United States.
Reviewed by: Zhao Yuhui and Jiang Yongfeng
Edited by: Li Haibo